Dosing once every 2 weeks with ENJAYMO1
Patients can receive an infusion 3 ways*

In office

At an infusion center
At home
*Subject to coverage requirements and physician determination.
The recommended dosing regimen for adults with Cold Agglutinin Disease (CAD) consists of an initial dose and a dose 1 week later, followed by 1 dose every 2 weeks. ENJAYMO is for IV infusion only.
Administer ENJAYMO at the recommended dosage regimen time points or within 2 days of these time points

Interruptions in ENJAYMO treatment
- If a dose is missed, administer as soon as possible and resume dosing every 2 weeks
- If the duration after the last dose exceeds 17 days, administer weekly for 2 weeks, with administration every 2 weeks thereafter
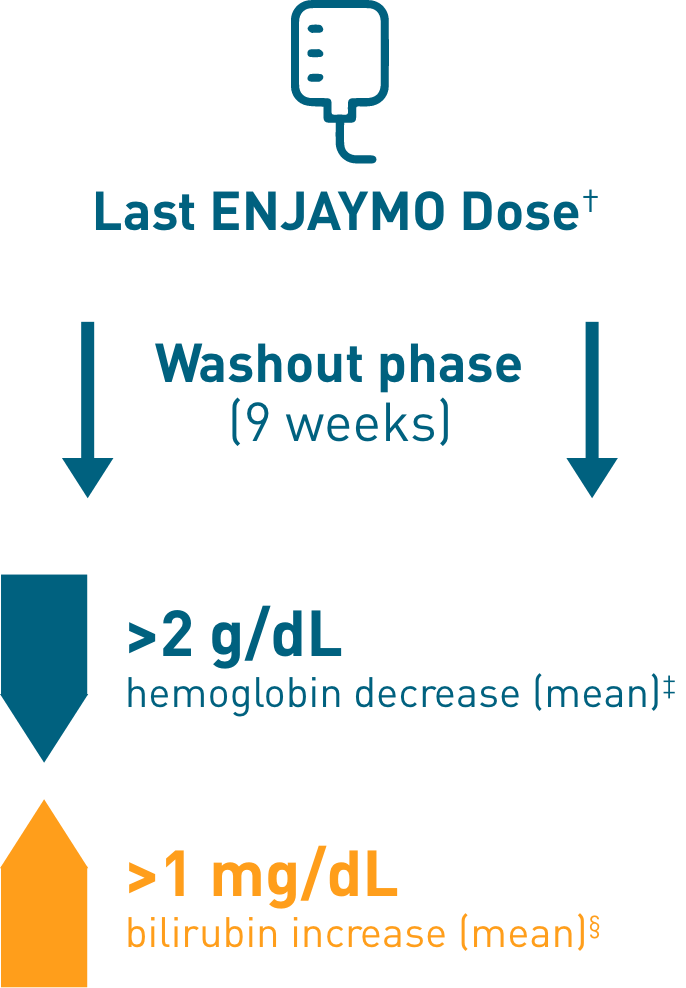
Chronic hemolysis and anemia returned after discontinuing ENJAYMO (n=39)
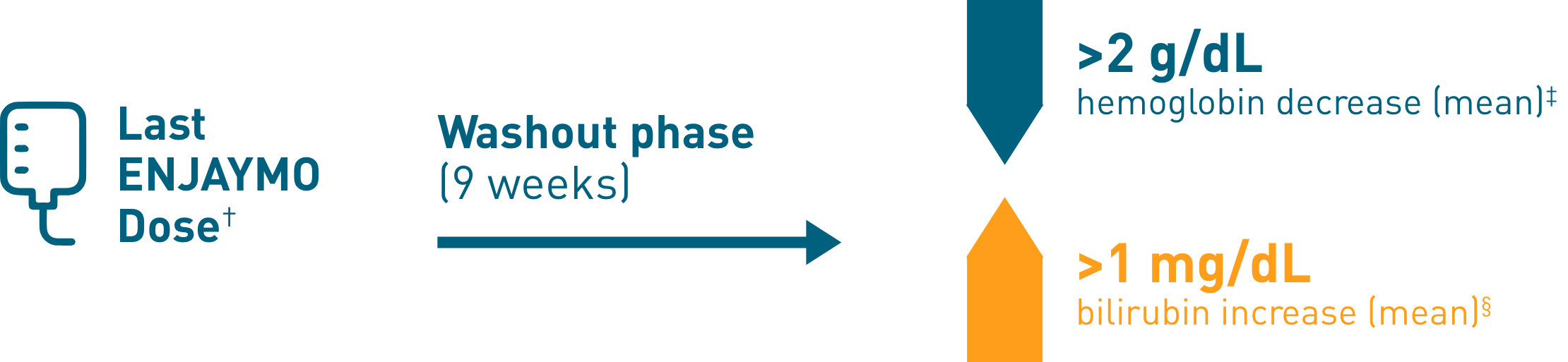
†Upon completion of Part B of CADENZA, a follow-up visit was completed 9 weeks after administration of the last dose of ENJAYMO.
‡Mean hemoglobin levels decreased 2.41 g/dL [SE: 0.373].
§Mean bilirubin increased 1.27 mg/dL.
Administration of ENJAYMO1
The dose for ENJAYMO infusion is weight based. ENJAYMO is supplied as one 1100 mg/22 mL (50 mg/mL) single-dose vial per carton. ENJAYMO can either be administered via an undiluted or diluted preparation.
WEIGHT-BASED INFUSION
6500 mg FOR PATIENTS 39 kg TO <75 kg
7500 mg FOR PATIENTS ≥75 kg
Dosing and infusion rate reference table for ENJAYMO undiluted
| Body weight range | Dose | ENJAYMO vials needed |
ENJAYMO volume |
Maximum infusion rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 39 kg to <75 kg | 6500 mg | 6 | 130 mL | 130 mL/hour‖ |
| ≥75 kg | 7500 mg | 7 | 150 mL | 150 mL/hour‖ |
Dosing and infusion rate reference table for ENJAYMO diluted in saline
| Body weight range |
Dose | ENJAYMO vials needed |
ENJAYMO volume |
NaCl diluent Volume |
Total volume |
Maximum infusion rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 39 kg to <70 kg | 6500 mg | 6 | 130 mL | 370 mL | 500 mL | 250 mL/hour |
| 70 kg to <75 kg | 6500 mg | 6 | 130 mL | 370 mL | 500 mL | 500 mL/hour‖ |
| ≥75 kg | 7500 mg | 7 | 150 mL | 350 mL | 500 mL | 500 mL/hour‖ |
║Patients with cardiopulmonary disease may receive the infusion over 120 minutes.
What to know before, during, and after an infusion1
Complete or update vaccination against encapsulated bacteria, including Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis (serogroups A, C, W, Y and B), according to current ACIP recommendations for patients receiving complement inhibitors at least 2 weeks prior to initiation of ENJAYMO.
If urgent ENJAYMO therapy is indicated in a patient who is not up to date with vaccines for Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis, administer these vaccines as soon as possible.
Vaccination does not eliminate the risk of serious encapsulated bacterial infections.
Monitor for infusion-related reactions like shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, nausea, flushing, headache, hypotension, chest discomfort, pruritus, rash, injection-site reaction, and dizziness.
Slow or stop the infusion if an infusion reaction occurs and institute appropriate supportive measures if signs of hypersensitivity occur.
Following initial infusion, monitor for 2 hours for signs or symptoms of an infusion and/or hypersensitivity reaction.
For subsequent ENJAYMO infusions, monitor for 1 hour for signs of an infusion reaction.
4 steps to infusing ENJAYMO1

Use aseptic technique to prepare ENJAYMO. Withdraw the calculated volume of ENJAYMO from the appropriate number of single-use vials based on the recommended dosage by weight in the dosing and infusion rate reference table.
Key Reminders
- To minimize foaming, do not shake ENJAYMO
- ENJAYMO is a clear to slightly opalescent and colorless to slightly yellow solution. Do not administer if discolored or if foreign particulate matter is present
- If preparing ENJAYMO for undiluted administration, the appropriate amount of ENJAYMO should be added to an empty infusion bag (130 mL or 150 mL depending on the dose)
- If preparing ENJAYMO for diluted administration, dilute with 0.9% Sodium Chloride to a total volume of 500 mL
- Discard unused portion of ENJAYMO

Allow the ENJAYMO infusion solution to adjust to room temperature 59 °F to 77 °F (15 °C to 25 °C) and administer within 8 hours.
Key Reminders
- Store ENJAYMO vials refrigerated at 36 °F to 46 °F (2 °C to 8 °C) in the original carton to protect from light. Do not freeze. Do not shake1
- If the ENJAYMO infusion solution is not used immediately, store refrigerated at 36 °F to 46 °F (2 °C to 8 °C)
- Total time from the time of preparation, including refrigeration, adjustment to room temperature, and the expected infusion time, should not exceed 36 hours1

Prime the infusion tubing with the dosing solution immediately before infusion and flush immediately following completion of the infusion with a sufficient quantity (approximately 20 mL) of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
Key Reminder
- In-line infusion warmers may be used, but should not exceed a temperature of 104 °F (40 °C)

Administer the ENJAYMO infusion over 1 to 2 hours (depending on the patient’s body weight) and only administer through a 0.2 micron in-line filter with a PES membrane.
Key Reminders
- Patients with cardiopulmonary disease may receive the infusion over 2 hours regardless of body weight
- Monitor for signs of infusion and/or hypersensitivity reactions per recommendations